Process
Contents: Overview | Transcription | Python Text Mining | Linking Primary Tag Sheet to Individual Transcripts
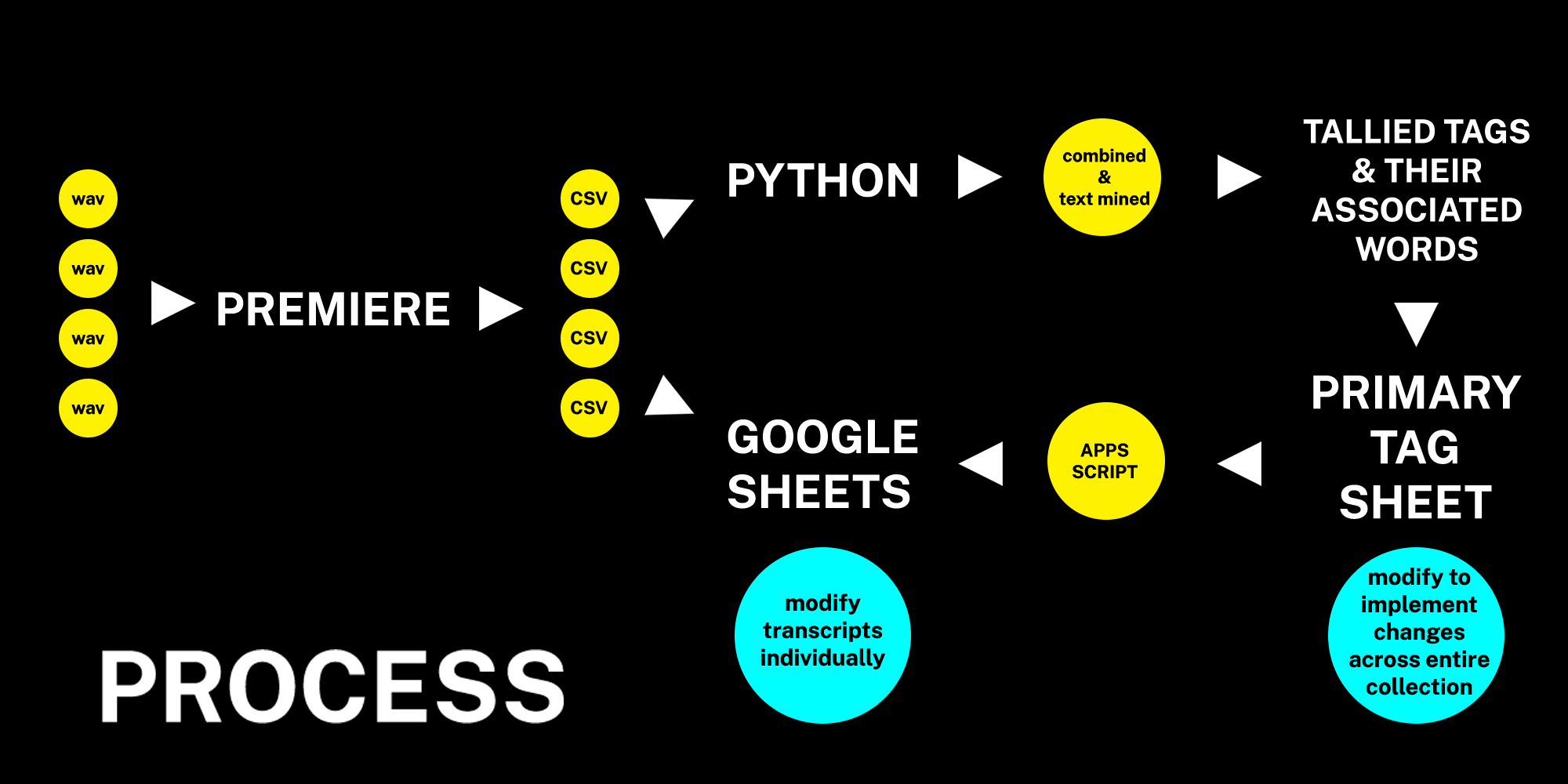
Overview
To summarize the process:
-
Audio is transcribed into CSV files by Premiere
-
CSVs are made into individual Google Sheets and also added to the Python Transcription Mining Tool
-
Within the tool, these items are combined and searched for all associated words and phrases built into the tool under different tag categories
-
The tool generates a tally of the these words and phrases, which is used to create the “Primary Tag Sheet” in another Google Sheet
-
Using the Apps Script function, all individual transcripts are linked to the primary tag sheet so their tag fields are automatically generated
-
New categories or associated words can be added or removed to the Primary Tag Sheet and these changes can be implemented across all individual transcripts by simply re-running the code
-
Individual changes can be implemented during the student worker led copy editing process to catch any data driven errors
✺
Transcription
Moving away from the speech to text tools the department had been working with, I tested Adobe Premiere’s transcription tools and found it uniquely well-suited for the OHD framework, with advantages including dramatically increased accuracy in differentiating speakers and transcribing dialogue, significantly faster transcription speed, and high privacy standards with GDPR compliance, ensuring all transcription material is stored locally and not uploaded to the cloud.[1]

That said, the tool is not perfect. While modern recordings in good conditions have extremely high transcription accuracy, poor quality recordings or interviews between two similar sounding people can require significant copyediting. Recent work by the Matt Miller of the Library of Congress has me very interested in creating custom speech to text tools using Whisper(.cpp) to possibly help improve on these inaccuracies.[2]
✺
Python Text Mining
After initial tests using the web based text mining tool Voyant, I wanted to create a text mining tool from scratch using Python that would allow me to identify specific words and phrases, create custom tagging categories and “stopwords”(words removed from text before processing and analysis) for each collection. Once the CSVs of the transcript are added to a folder in the Python workspace, the code imports text mining libraries such as Pandas, NLTK, TextBlob, and regular expressions for processing.
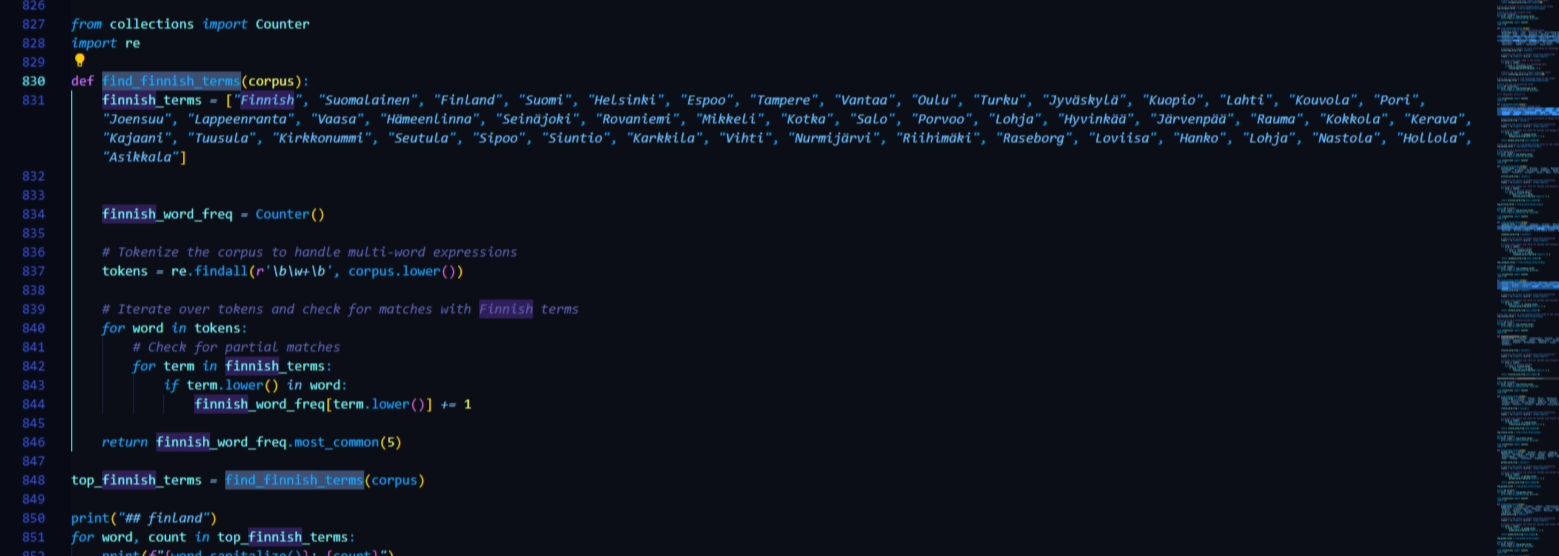
Below this header material in the Python file are three categories of tags: general, geographic and custom, which contain twenty subsections each and these subsections contain 50 associated words or phrases that are being identified throughout the combined corpus and ultimately tallied to produce the output shown here:
✺

See Appendix 1 for an excerpt of the this script or visit the Git to view in full.
Linking Primary Tag Sheet to Individual Transcripts
This data is then entered into a “primary tag sheet” also in Google Sheets. After formatting their transcripts, the student worker opens the Apps Script extension and enters a string of code (see Appendix 2). After making two minor adjustments based on the URL of their transcript, it will be linked to the Primary Tag Sheet.
✺